Debt from student loans has been a topic of discussion and concern for a very long time.
Many students and their families rely on loans to pay for their education because the expense of higher education is on the rise.
Borrowers must be aware of the different loan kinds and their benefits.
This blog will delve into the controversy over whether student loans are secured or unsecured as we examine the special characteristics of educational finance and how they impact borrowers.
What are Secured and Unsecured Loans?
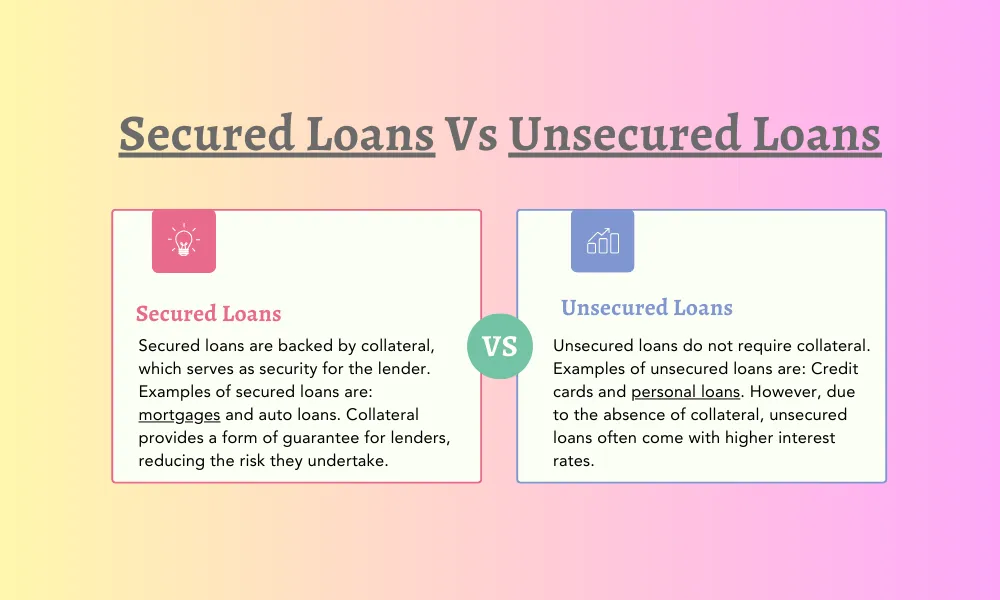
Secured loans are backed by collateral, which serves as security for the lender. Examples of secured loans are: mortgages and auto loans. Collateral provides a form of guarantee for lenders, reducing the risk they undertake.
In contrast, unsecured loans do not require collateral. Examples of unsecured loans are: Credit cards and personal loans. However, due to the absence of collateral, unsecured loans often come with higher interest rates.
Is Student Loan Secured or Unsecured?
Student loans are generally considered unsecured loans. According to the applicant’s creditworthiness and the assumption that the borrower will be able to repay the loan with future earnings from both employment and education, student loans are frequently given.
If a borrower fails to repay a student loan, the lender generally cannot seize any specific property as collateral.
Also See: How To Get a Loan at 18?
Why are student loans considered unsecured?
Student loans are considered unsecured because they are typically not backed by collateral like property or assets.
Unlike secured loans, which have collateral to secure repayment, student loans rely primarily on the borrower’s promise to repay the debt based on their future income potential and creditworthiness.
What is the difference between secured and unsecured debt student loan?
| Aspect | Secured Debt Student Loan | Unsecured Debt Student Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Collateral Requirement | Requires collateral, such as a car or property, which can be seized if the borrower defaults on the loan. | Does not require collateral; no assets are at risk if the borrower defaults on the loan. |
| Interest Rates | Generally lower interest rates due to the presence of collateral, which reduces the lender’s risk. | Generally higher interest rates since there is no collateral to secure the loan. |
| Eligibility Criteria | May have less stringent eligibility requirements since the collateral serves as a form of security for the lender. | May have more stringent eligibility requirements due to the higher risk associated with the absence of collateral. |
| Borrowing Limits | Tends to have higher borrowing limits since the collateral can provide additional assurance to the lender. | Tends to have lower borrowing limits due to the absence of collateral, which increases the lender’s risk. |
| Repayment Terms | Repayment terms may be longer, allowing for more affordable monthly payments. | Repayment terms may be shorter, resulting in higher monthly payments. |
| Default Consequences | If the borrower defaults, the lender can seize the collateral to recover the outstanding loan amount. | If the borrower defaults, the lender has limited options for recovery and may pursue legal action or use collection agencies. |
| Examples | Home Equity Loan, Car Title Loan | Federal Stafford Loan, Private Student Loan |
What kind of loan is a federal student loan?
A federal student loan is a type of loan offered by the U.S. Department of Education to help students pay for their education.
These loans are specifically designed for students and offer various benefits such as:
- fixed interest rates,
- flexible repayment options,
- potential loan forgiveness programs.
They are funded and regulated by the federal government, making them different from private student loans.
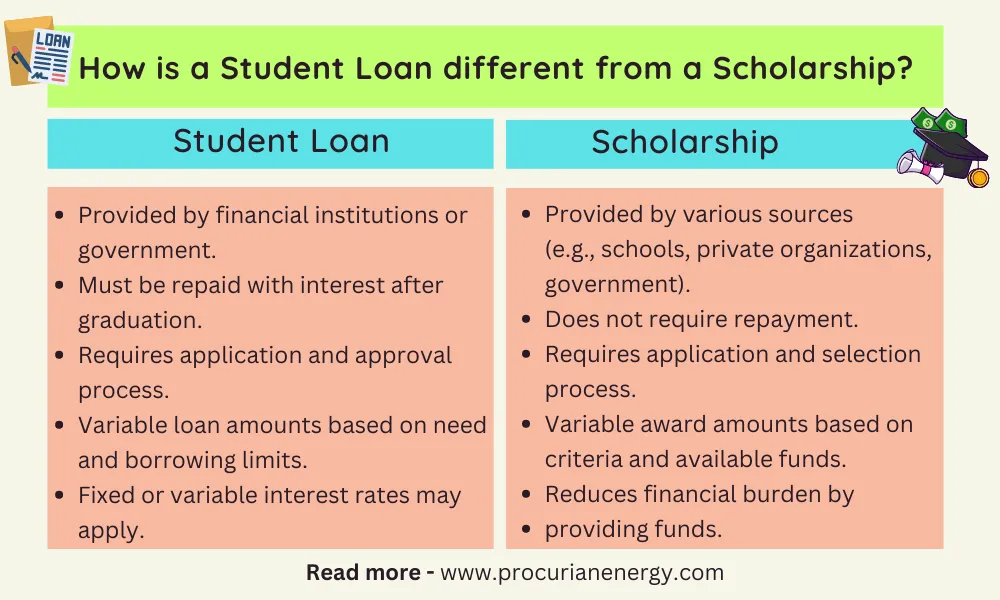
Also See: How is a Student Loan different from a Scholarship?
What is the difference between a student loan and a federal student loan?
| Student Loan | Federal Student Loan | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A loan offered by private lenders or banks | A loan provided by the U.S. Department of Education through federal programs |
| Lender | Private lenders or banks | U.S. Department of Education |
| Application Process | Application directly with the lender | FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) is required. |
| Interest Rates | Set by the lender | Fixed interest rates set by the federal government |
| Repayment Options | Varies by lender | Various flexible repayment options available such as income-driven repayment plans |
| Borrower Benefits | Varies by lender | Borrower benefits and loan forgiveness programs may be available |
| Loan Limits | Varies by lender | Federal loan limits depending on the type of loan and academic level |
| Credit Check | Often requires a credit check | No credit check required for most federal loans |
| Subsidized Loans | Not applicable | Federal loans may offer subsidized options based on financial need |
| Loan Forgiveness | Depends on the lender’s policies | Certain federal loans may be eligible for loan forgiveness programs |
| Cosigner Option | May require a cosigner for approval | Generally, no cosigner required for most federal loans |
| Loan Servicer | Determined by the lender | Assigned by the U.S. Department of Education |
Which are the easiest type of student loans to get?
Direct Subsidized Loans are typically the easiest type of student loans to obtain.
These loans are provided by the government and do not require a credit check or a cosigner.
They have low interest rates and flexible repayment options.
What GPA is required for student loans?
Students must have a 2.0 GPA (grade point average) in order to be considered for a federal student loan.
Do I get student loan forgiveness?
To qualify for loan forgiveness, you must have federal student loans and earn less than $125,000 (or $250,000 per household) annually. Those borrowers could be qualified for a debt cancellation of up to $10,000.
Are student loans automatically forgiven after 25 years?
No, student loans are not automatically forgiven after 25 years.
However, certain student loan relief options like the Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans, allow borrowers to be eligible for loan forgiveness after making payments for 20 to 25 years.
Can You Convert Unsecured student Loans to Secured Loans?
No, it is generally not possible to convert unsecured student loans to secured loans.
Unsecured student loans are typically granted based on the borrower’s creditworthiness and do not require collateral.
In contrast, secured loans are backed by collateral, such as property or assets.
Converting student loans to secured loans would require a significant change in the terms and conditions of the loan agreement, which is not a common practice in the student loan industry.
How risky is an unsecured loan?
An unsecured loan carries a certain degree of risk for both borrowers and lenders.
Borrowers with weaker credit histories may be offered higher interest rates, reflecting the increased risk to the lender.
For borrowers, the risk lies in the potential inability to repay the loan, which can result in damaged credit, collection actions, and legal consequences.
Lenders face the risk of losing their investment if the borrower defaults on the loan.
Why is it so hard to pay off student loans?
It is often challenging to pay off student loans due to several factors.
- The cost of education has risen significantly, forcing many students to take out substantial loans to finance their studies. This leads to higher loan balances.
- The interest rates on student loans can be relatively high, accruing over time and increasing the overall amount owed.
- Many graduates face difficulties in finding well-paying jobs immediately after graduation, making it harder to meet their loan obligations.
- The combination of high loan balances, interest rates and limited income can create a financial burden that takes years to repay, making it challenging to clear student loan debts.
How long does the average person take to pay off student loans?
Generally, the standard repayment period for federal student loans is 10 years.
Private student loans may have different repayment terms, ranging from 5 to 20 years.
The average time it takes for an individual to pay off their student loans can vary widely depending on factors such as loan amount, interest rates, repayment plans and personal financial circumstances.
Can student loans seize your bank account?
Student loans alone cannot seize your bank account without a legal process.
However, if you default on your federal student loans, the government has the authority to initiate a process called “administrative wage garnishment” to collect the outstanding debt. This allows them to withhold a portion of your wages directly from your paycheck. While they cannot seize your bank account directly, they may still garnish your wages, which could affect the funds in your account.
Private student loan lenders may pursue legal action to obtain a judgment against you, which could potentially lead to bank account garnishment but this varies by jurisdiction and specific circumstances.
It’s crucial to stay informed about your rights and options if you’re struggling with student loan debt.
Do student loans destroy your credit?
Student loans can affect your credit, but they don’t necessarily destroy it.
Timely payments can actually help build a positive credit history.
If you make timely payments and manage your debt responsibly, student loans can actually help build your credit over time.
How long does it take to pay off 100k student loans?
Assuming a fixed interest rate and regular monthly payments, it could take anywhere from 10 to 15 years to fully repay the loan.
The monthly payment on a $100,000 student loan with a 5% interest rate and a 10 year repayment term, the estimated monthly payment would be around $1,060.
| Loan amount | Interest rate | Loan duration | Monthly payment |
|---|---|---|---|
| $100,000 | 5% | 10 years | $1060 |
How much is the monthly payment on a $80000 student loan?
The monthly payment on an $80,000 student loan with a fixed interest rate of 5% and with a 10-year term, the approximate monthly payment would be around $844.
| Loan amount | Interest rate | Loan duration | Monthly payment |
|---|---|---|---|
| $80,000 | 5% | 10 years | $844 |
How much is the monthly payment on a $70,000 student loan?
The monthly payment on a $70,000 student loan with a 5% interest rate and a 10-year repayment term, the approximate monthly payment would be around $742.
| Loan amount | Interest rate | Loan duration | Monthly payment |
|---|---|---|---|
| $70,000 | 5% | 10 years | $742 |
How much is the monthly payment on a $50,000 student loan?
The monthly payment on a $50,000 student loan with a 5% interest rate and a standard 10-year loan would result in a monthly payment of around $530
| Loan amount | Interest rate | Loan duration | Monthly payment |
|---|---|---|---|
| $50,000 | 5% | 10 years | $530 |
What would it cost per month to repay a $35000 loan?
The cost per month to repay a $35,000 loan with a 5% interest rate and a 5-year term, the monthly repayment amount would be approximately $660.
| Loan amount | Interest rate | Loan duration | Monthly payment |
|---|---|---|---|
| $35,000 | 5% | 5 years | $660 |
What are 3 reasons student loans should be avoided?
Three reasons student loans should be avoided are:
1. Debt burden – Student loans can saddle individuals with a significant financial burden for years or even decades, affecting their ability to save, invest or pursue other life goals.
2. Interest accumulation – Loans accrue interest over time, increasing the overall amount owed. This can result in individuals paying back much more than they initially borrowed.
3. Limited flexibility – Student loan payments can restrict financial flexibility, making it harder to make career choices, start a business or handle unexpected expenses. It may also delay major life milestones like buying a home or starting a family.